3D Printing
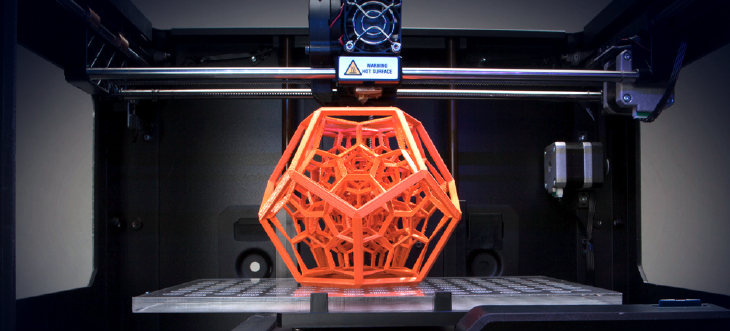
While the concept of 3D printing has been around since the 1970’s, it has only been in recent years the technology has flourished; both commercially and in the consumer market. In fact, 3D printing still isn’t mainstream enough for Webster to define. However, the term can be found on Wikipedia. Wikipedia’s definition for 3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, is “a process of making a three-dimensional solid object of virtually any shape from a digital model.”
Commercial 3D Printing
Commercial 3D printing has been around since the early 1980s. Large companies and universities adopted the technology mainly for rapid prototyping and research purposes. Today, the number of companies and schools using commercial 3D printers is growing quickly and the printers are being used for rapid prototyping, rapid manufacturing, and mass customization. Commercial 3D printing is being used in engineering, the medical and dental industry, fashion, footwear, eyewear, jewelry, military, education, and more.
Commercial printers use various technologies and print in a variety of materials including ABS plastic, sandstone-like materials, UV cured resins, nylon, and alloys like gold, silver, stainless steel, and titanium. Scientists are now experimenting with bio-printing, which is 3D printing with living cells.
The cost of commercial 3D printers varies. Some printers start at a few thousand dollars, with some costing more than a million dollars.
Consumer 3D Printing
The popularity of consumer 3D printing has grown over the last couple of years. What started out as a fun project for hobbyists and tinkerers, is now becoming mainstream. There are currently over 130 companies building consumer 3D printers with more startup companies entering the market every year.
Most consumer 3D printers use fused disposition modeling (FDM). This means the printers squeeze heated material, usually plastic, through a nozzle. The printer lays the material down in layers and as the material cools, it hardens and sticks to the previous layer.
Most consumer 3d printers use ABS or PLA plastic to print objects.
The cost for consumer printers is between $500 and go up to a few thousand.
3D Printing Technologies
There are various technologies used in 3D printing with more coming out each year and the technologies that exist are advancing rapidly. Some of the technologies that exist in 3D printing are binder jetting, laser sintering metal (LSM), fused disposition modeling (FDM), electron beam freeform fabrication (EBF3), laminated object manufacturing (LOM), digital light processing (DLP), stereolithography (SLA), and electron beam melting (EBM).
History of 3D Printing
Important dates in 3D printing:
1984 – The birth of 3D printing
1992 – First SLA machine is produced by 3D Systems
1999 – 3D printed organ is implanted in humans
2002 – A working kidney is 3D printed
2005 – RepRap is born
2006 – SLS leads to mas customization in manufacturing
2008 – RepRap project releases Darwin which is the first self-replicating 3D printer
2008 – Major breakthroughs for 3D printed prosthetics
2009 – First 3D printed blood vessel
2011 – First 3D printed robotic aircraft
2011 – First 3D printed car
2011 – 3D printing in gold and silver
2012 – 3d printed prosthetic jaw is implanted
3D Printing in the Media
CSI: NY – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NKhpa5Nt6Ck
Big Bang Theory – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tsz9GUZv1IA
To learn more about the latest in 3D Printing, check out our 3D printing.