Orthophoto Maps
Orthophoto maps, also known as orthophotographs or orthomosaics, are aerial or satellite images that have been corrected for distortion and perspective to produce a map-like image that accurately represents the Earth’s surface. Orthophoto maps are widely used for a variety of applications, including urban planning, land use analysis, natural resource management, and emergency response.
Types of Orthophoto Maps
There are two main types of orthophoto maps: true orthophotos and digital orthophotos.
- True Orthophotos: True orthophotos are created by photographing the Earth’s surface from multiple angles using a special camera that eliminates distortion and perspective effects. This method produces highly accurate maps that are used for precision applications such as land surveying, engineering, and construction. The camera used for true orthophotos is typically equipped with a tilt and shift mechanism, which allows the camera to capture multiple images of the same area from different angles. These images are then combined to produce a single, highly accurate map.
True orthophotos have several advantages over digital orthophotos. They are highly accurate, with a positional accuracy of less than one meter. They are also able to capture fine details such as individual buildings and trees, making them useful for applications such as urban planning and land surveying. However, true orthophotos can be more expensive to produce than digital orthophotos, as they require specialized equipment and highly skilled operators.
- Digital Orthophotos: Digital orthophotos are created by digitally combining aerial or satellite images that have been geometrically corrected. This method is more efficient and cost-effective than true orthophotos, as it does not require specialized equipment or highly skilled operators. Digital orthophotos are often used for applications such as environmental management, transportation planning, and emergency response.
Digital orthophotos are created using a process called photogrammetry, which involves analyzing multiple overlapping images of the same area to create a highly accurate map. The images used for digital orthophotos are typically captured by drones, airplanes, or satellites, and are corrected for distortion and perspective using specialized software.
Digital orthophotos have several advantages over true orthophotos. They are less expensive to produce, as they do not require specialized equipment or highly skilled operators. They are also able to cover larger areas than true orthophotos, making them useful for applications such as land use analysis and natural resource management. However, digital orthophotos may not be as accurate as true orthophotos, with a positional accuracy of approximately one to three meters.
Both true orthophotos and digital orthophotos have their own advantages and disadvantages. True orthophotos are highly accurate but can be more expensive to produce, while digital orthophotos are more cost-effective but may not be as accurate. The choice between the two types of orthophoto maps depends on the specific application and the level of accuracy required. Regardless of the type, orthophoto maps are a valuable tool for a wide range of industries and applications.
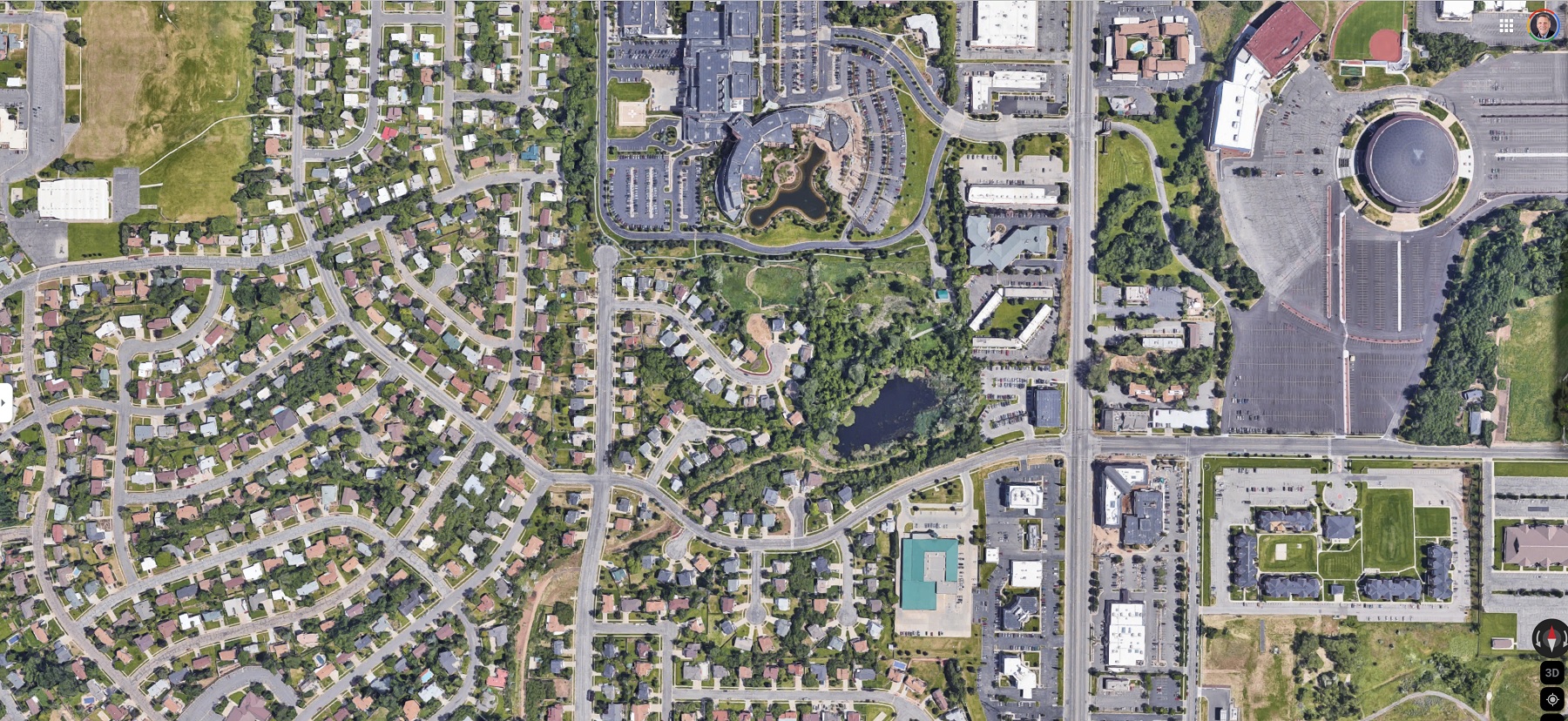
Uses of Orthophoto Maps
ere are some of the many uses of orthophoto maps:
Urban Planning: Orthophoto maps are used to map out urban areas, including roads, buildings, and other infrastructure. These maps can be used to plan new developments, assess existing infrastructure, and analyze population trends.
Land Surveying: Orthophoto maps are used for land surveying, providing highly accurate measurements of land features such as boundaries, elevation, and topography.
Environmental Management: Orthophoto maps are used to monitor changes in the environment, including changes in vegetation, water quality, and land use. These maps can help to identify areas that require conservation efforts and can be used to monitor the effectiveness of conservation programs.
Transportation Planning: Orthophoto maps are used to plan transportation routes, map road networks, and analyze traffic patterns. These maps can be used to optimize transportation systems, improve safety, and reduce congestion.
Agriculture: Orthophoto maps are used to monitor crop health, estimate crop yields, and plan irrigation and fertilizer applications. These maps can help farmers to optimize their crop production and reduce waste.
Emergency Response: Orthophoto maps are used to plan for and respond to natural disasters, such as floods or wildfires. These maps can be used to identify areas that are at risk, assess damage after a disaster has occurred, and coordinate emergency response efforts.
Mining: Orthophoto maps are used in mining operations to map out mineral deposits, plan extraction methods, and monitor changes in the environment caused by mining activities.
Archaeology: Orthophoto maps are used in archaeology to map out archaeological sites, plan excavations, and analyze the layout of ancient cities and settlements.
Features of Orthophoto Maps
Orthophoto maps have several features that make them useful for a wide range of applications. Some of these features include:
Accurate Georeferencing: Orthophoto maps are accurately georeferenced, meaning that they are tied to a specific location on the Earth’s surface. This allows them to be used for precise measurements and analysis.
High Resolution: Orthophoto maps can have very high resolution, allowing for detailed analysis of small features on the Earth’s surface.
Multi-Spectral Data: Many orthophoto maps are created using multi-spectral data, which can provide information on a wide range of features, including vegetation health, water quality, and land use.
Digital Format: Orthophoto maps are typically available in digital format, which allows for easy storage, sharing, and analysis.
Benefits of Orthophoto Maps
There are several benefits to using orthophoto maps, including:
Accurate Data: Orthophoto maps provide accurate and precise data that can be used for a variety of applications.
Cost-Effective: Orthophoto maps are often more cost-effective than traditional surveying methods, as they can cover large areas in a relatively short amount of time.
Easy to Use: Orthophoto maps are often available in digital format, which makes them easy to use and share.
Real-Time Monitoring: Orthophoto maps can be updated in real-time, allowing for quick and accurate analysis of changes on the Earth’s surface.
Learn more about Maps
- Topographical Maps: Representation of the physical features of a region or area.
- Contour Maps: Representation of the contours of the land surface or ocean floor.
- Raised Relief Maps: Representation of land elevations with raised features indicating landforms.
- Terrain Maps: Representation of the physical features of a terrain or landmass.
- USGS Topographic Maps: Representation of topographic features and land elevations based on USGS data.
- USGS Historical Topographic Maps: Representation of historical topographic maps created by the USGS.
- Watershed Maps: Representation of the areas where water flows into a particular river or lake.
- Elevation Maps: Representation of land and water elevations with high precision.
- Physical Maps: Representation of physical features of the Earth’s surface such as landforms, oceans, and plateaus.
- Bathymetric Maps: Representation of the topography and features of the ocean floor.
- NOAA Maps: Representation of atmospheric, oceanographic, and environmental data by NOAA.
- Nautical Maps: Representation of the underwater features and depth of an area for navigation purposes.
- Geologic Maps: Representation of the geologic features of an area such as rock types, faults, and folds.
- Satellite Maps: Representation of earth from high-definition satellite imagery.
History of Orthophoto Maps
Orthophoto maps have a rich history that dates back over a century. The first orthophoto map was created in 1908 by the French army, and since then, the technology has continued to advance and evolve. Here is a brief history of the development of orthophoto maps:
Early History In the early 1900s, the French army began using aerial photography to map out the battlefield during World War I. They soon realized that the photos were distorted due to the perspective effect of the camera, and they began experimenting with different methods to correct the distortion. In 1908, they created the first orthophoto map, which used a process called rectification to correct the perspective distortion and create an accurate map of the terrain.
Advancements in Technology: In the decades that followed, the technology for creating orthophoto maps continued to advance. During World War II, aerial photography became more widespread and advanced, and orthophoto maps were used extensively for military operations. In the 1960s, the development of computers and digital imaging technology revolutionized the field of photogrammetry, making it possible to create digital orthophoto maps.
Modern Applications Today: Orthophoto maps are used in a wide range of applications, from urban planning and land surveying to agriculture and environmental management. With advancements in satellite and drone technology, it is now possible to create orthophoto maps with even greater accuracy and detail than ever before. One notable advancement in the field of orthophoto mapping is the development of geographic information systems (GIS), which allow users to analyze and manipulate spatial data. The integration of orthophoto maps with GIS has opened up new possibilities for applications such as transportation planning, emergency response, and urban development. Another recent development in orthophoto mapping is the use of LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology. LiDAR uses laser pulses to create highly detailed, 3D maps of the Earth’s surface, which can be combined with orthophoto maps to create even more accurate and detailed maps.
Orthophoto maps have also become increasingly accessible to the general public, thanks to the availability of online mapping services such as Google Maps and Bing Maps. These services allow users to view and interact with orthophoto maps from anywhere in the world, making them an invaluable tool for navigation, travel planning, and exploration.
In recent years, the use of orthophoto maps has also expanded to include new applications such as virtual reality and augmented reality. For example, orthophoto maps can be used to create immersive virtual environments for training simulations or to enhance the experience of exploring historical sites.
To learn more about the latest in 3D Maps, check out 3D Maps.