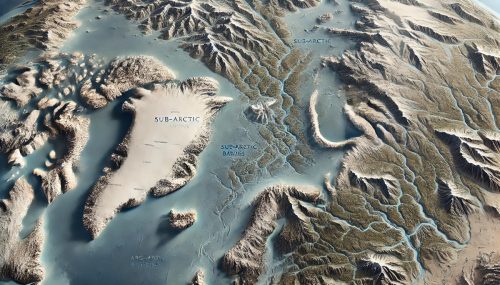
Lake Huron Watershed Map
Lake Huron Watershed Map
We Build Custom 3D Watershed Maps
Lake Huron Watershed Map: Understanding the Hydrology and Importance of One of the Great Lakes
Lake Huron is the second-largest of the five Great Lakes in North America, known for its vast expanse of freshwater, rich ecosystems, and scenic shorelines. Spanning approximately 23,000 square miles, Lake Huron has a depth that reaches over 700 feet, making it not only one of the most significant freshwater lakes in the world but also a critical component of the ecosystem of the Great Lakes Basin. The Lake Huron Watershed, which encompasses the lake itself and its surrounding river systems, wetlands, and tributaries, plays an essential role in sustaining diverse habitats, supporting local economies, and maintaining the quality of water flowing into the lake.
The Lake Huron Watershed Map provides invaluable insights into the hydrology of this vast region, helping experts, land planners, conservationists, and policymakers understand the movement of water through the watershed and the impact it has on the environment. The map highlights key water systems, including the numerous rivers and streams that flow into the lake, as well as the wetlands, forests, and riparian zones that play a role in maintaining water quality, supporting biodiversity, and preventing soil erosion. By analyzing the watershed map, stakeholders can make informed decisions regarding water management, conservation, and land-use planning to preserve the integrity of this vital natural resource.
In this blog, we will take a deep dive into the Lake Huron Watershed, exploring its hydrology, geography, and ecological significance. We will also examine the role of the Lake Huron Watershed Map in supporting sustainable water management and conservation efforts. Furthermore, we will explore the technologies behind creating the Lake Huron Watershed 3D Map, focusing on how advanced mapping tools and techniques are used to enhance our understanding of the watershed and aid in its preservation.
Geography and Hydrology of the Lake Huron Watershed: Understanding the Flow of Water and Its Impact
The Lake Huron Watershed spans over 50,000 square miles, covering parts of the Canadian province of Ontario and the U.S. state of Michigan. The watershed is defined by the flow of water into Lake Huron, as well as the surrounding land areas that contribute to the water’s movement. The watershed includes numerous tributaries, streams, rivers, and wetlands that feed into the lake, as well as the drainage areas surrounding the lake’s shores. These waterways play a crucial role in shaping the hydrology of the region and maintaining the ecological balance of the lake.
One of the primary rivers in the Lake Huron Watershed is the St. Clair River, which connects Lake Huron to Lake Erie. This river serves as a vital outlet for the water that flows into Lake Huron, and it is also one of the most important rivers for shipping and transportation in the region. The St. Clair River is fed by a number of tributaries that drain the surrounding landscape, contributing to the overall flow of water into the lake. Similarly, the Saginaw River in Michigan is another major tributary that drains into Lake Huron, bringing water from the Saginaw Bay region and contributing to the overall water quality of the lake.
In addition to these rivers, the watershed includes several smaller rivers, streams, and creeks that flow into the lake. These water systems are essential for replenishing the water levels of Lake Huron, maintaining water quality, and supporting aquatic habitats. The numerous streams and tributaries that feed into the lake help distribute water across the region, with each river contributing to the overall health of the lake’s ecosystem.
Lake Huron’s hydrology is affected by a variety of natural and human-induced factors. Seasonal changes in precipitation, snowmelt, and evaporation all impact the water levels of the lake. During periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt in the spring, rivers and streams feeding into Lake Huron experience higher-than-normal flows, which can result in increased water levels in the lake itself. During dry seasons or periods of drought, the water levels may decrease, reducing the available freshwater supply and affecting the quality of the water.
Human activity has also significantly influenced the hydrology of the Lake Huron Watershed. Urbanization, industrial development, and agriculture have all contributed to changes in water flow patterns, water quality, and the overall health of the watershed. The construction of dams, levees, and flood control infrastructure has altered the natural movement of water in the region, affecting river channels and groundwater levels. Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and urban stormwater has also impacted water quality, leading to increased nutrient levels and the risk of harmful algal blooms.
Ecological Importance of the Lake Huron Watershed: Protecting Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
The Lake Huron Watershed is home to a diverse array of ecosystems that provide essential habitat for numerous species of plants, animals, and aquatic organisms. The region’s wetlands, forests, rivers, and shoreline habitats are crucial for maintaining biodiversity and supporting a wide range of species. From migratory birds to native fish species, the ecosystems in the watershed provide critical resources for a variety of wildlife, contributing to the ecological health of the region.
Wetlands in the Lake Huron Watershed, particularly along the shoreline and in the Saginaw Bay area, play a vital role in supporting aquatic ecosystems. These wetlands act as natural filters, trapping pollutants, sediments, and excess nutrients before they can reach the lake. This helps maintain water quality in Lake Huron and supports the health of the lake’s aquatic life. Wetlands also provide essential breeding and feeding grounds for migratory birds, such as ducks and geese, and serve as habitat for numerous amphibians and reptiles.
The forests and riparian zones along the rivers and streams of the watershed are equally important for maintaining water quality and biodiversity. These forests provide habitat for a wide range of mammals, such as white-tailed deer, foxes, and coyotes, and they also support populations of birds, insects, and other wildlife. The riparian zones along the rivers help stabilize the banks of the waterways, reduce erosion, and improve water filtration, ensuring that the rivers and streams feeding into Lake Huron remain clean and healthy.
Lake Huron itself is home to a wide range of fish species, including lake trout, walleye, and smallmouth bass, which support both recreational and commercial fishing industries in the region. These fish species, along with other aquatic organisms such as mussels and zooplankton, play important roles in the food web of the lake and contribute to the overall health of the ecosystem. However, the lake is also facing challenges from invasive species such as zebra mussels and the sea lamprey, which disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystem and threaten the health of native fish populations.
The Lake Huron Watershed is also home to unique habitats such as the Ontario Carolinian zone and the Michigan coastal wetlands, which provide refuge for rare and endangered species, including the endangered Lake Huron yellow perch and the Eastern Massasauga rattlesnake. The protection of these habitats is critical for preserving biodiversity in the region and ensuring that native species continue to thrive.
The Role of the Lake Huron Watershed Map: Water Quality Monitoring, Flood Control, and Conservation
The Lake Huron Watershed Map is an essential tool for understanding the flow of water in the region, monitoring water quality, and supporting conservation efforts. The map provides a detailed representation of the watershed’s rivers, streams, tributaries, wetlands, and other natural features, helping stakeholders track water movement and identify areas that may be at risk of flooding, pollution, or habitat degradation.
Water quality monitoring is one of the most important functions of the Lake Huron Watershed Map. The map allows researchers and environmental managers to track water temperature, nutrient levels, dissolved oxygen, and pollutant concentrations at various points in the watershed. By analyzing this data, stakeholders can identify areas where water quality is declining and take action to address the sources of pollution. This is critical for maintaining the health of the lake’s ecosystems, protecting aquatic life, and ensuring that the lake remains a safe and reliable water source for surrounding communities.
Flood control is another key area where the Lake Huron Watershed Map plays a vital role. The map helps predict flood events by tracking water flow in the tributaries and rivers feeding into the lake. By analyzing rainfall patterns, snowmelt, and river flow data, the map allows flood control authorities to identify areas at risk of flooding and implement strategies to reduce the impact of high-water events. This is essential for protecting communities, infrastructure, and agricultural lands from the damage caused by flooding.
Conservation efforts in the Lake Huron Watershed are also supported by the map. By identifying critical habitats, wetlands, and riparian zones, the map helps guide land-use decisions and prioritize areas for protection or restoration. The map also helps track changes in land use, such as urban development or agricultural expansion, which may have negative impacts on water quality and habitat health. In this way, the map supports efforts to protect the biodiversity of the watershed and ensure that it remains a sustainable resource for future generations.
How Lake Huron Watershed 3D Maps Are Fabricated: The Role of LiDAR, Satellite Imagery, and GIS
Creating an accurate and detailed 3D map of the Lake Huron Watershed requires the integration of several advanced technologies, including LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), satellite imagery, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS). These technologies work together to produce high-resolution, interactive maps that provide valuable insights into the watershed’s hydrology, topography, and ecology.
LiDAR is one of the primary technologies used to create the digital elevation model (DEM) of the watershed. LiDAR uses laser pulses to measure the distance from the sensor to the ground, generating precise three-dimensional data that captures the elevation changes and topographic features of the landscape. This data is essential for understanding water flow, flood-prone areas, and the distribution of wetlands and riparian zones.
Satellite imagery is used to capture high-resolution images of the watershed from above. These images provide valuable information on land cover, vegetation, water bodies, and other features of the landscape. By analyzing these images, researchers can monitor changes in land use, track vegetation health, and assess the impact of human activities on water quality and ecosystems.
GIS software is used to integrate the data collected from LiDAR and satellite imagery into a single, comprehensive map. GIS allows for the creation of layered maps that combine different types of data, such as streamflow, water quality, land use, and ecological information. These interactive maps enable stakeholders to explore the watershed in three dimensions, simulating water movement, flood events, and the effects of land use changes on water quality and ecosystem health.
The Future of Lake Huron Watershed Maps: Enhancing Sustainability and Resilience
As the Lake Huron Watershed faces increasing challenges from climate change, urbanization, and pollution, the role of 3D watershed maps will become even more critical. Advances in real-time data integration, predictive modeling, and climate simulations will enhance the accuracy of these maps, enabling better decision-making for water management, flood control, and habitat restoration. These maps will continue to play a key role in ensuring the long-term sustainability of the Lake Huron Watershed and its ecosystems.
In conclusion, the Lake Huron Watershed is a vital natural resource that supports diverse ecosystems, provides fresh water for millions of people, and plays a key role in regional economies. The Lake Huron Watershed Map, with its advanced technologies and detailed representation of the watershed, is essential for understanding water flow, managing water quality, and supporting conservation efforts. Through the use of LiDAR, satellite imagery, and GIS, these maps provide valuable insights into the hydrology, ecology, and land use of the watershed, helping stakeholders make informed decisions for sustainable management and protection. As the region faces increasing environmental challenges, the continued development of these maps will help ensure the resilience and health of the Lake Huron Watershed for future generations.
Check out WhiteClouds’ 3D Maps for more information on Lake Huron watershed maps.