What Is a Plateau?
What Is a Plateau?
We Build Custom 3D Maps
Did you know we make
custom
3D Raised Relief Maps
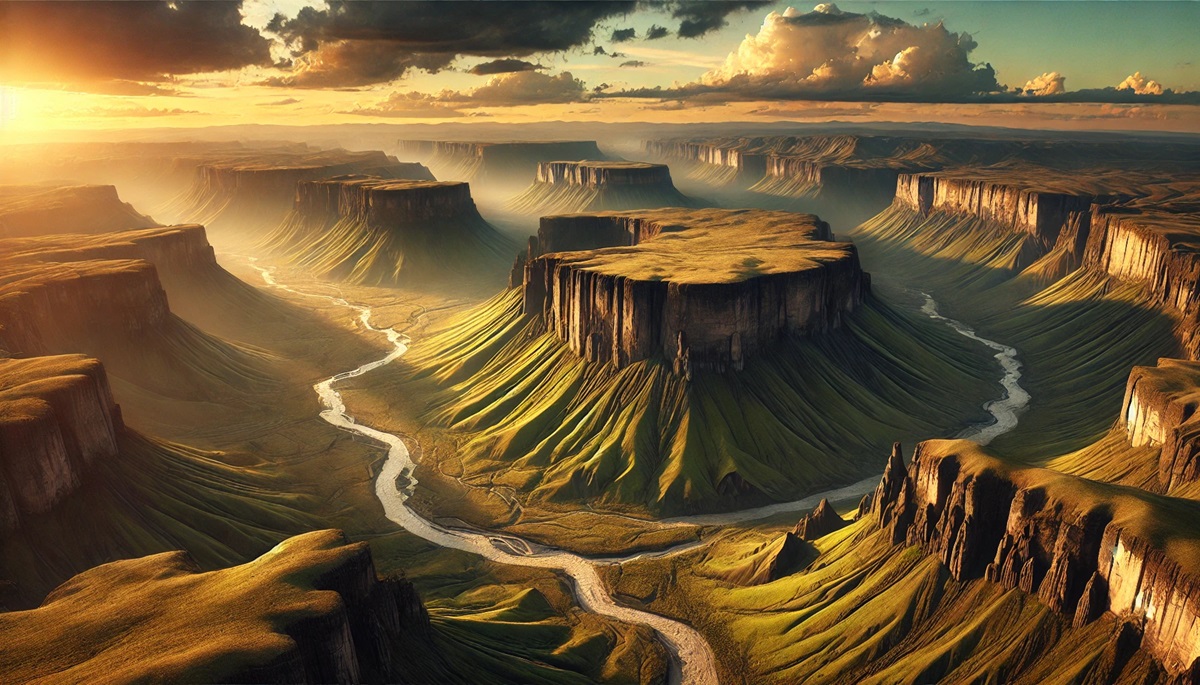
What is a Plateau?
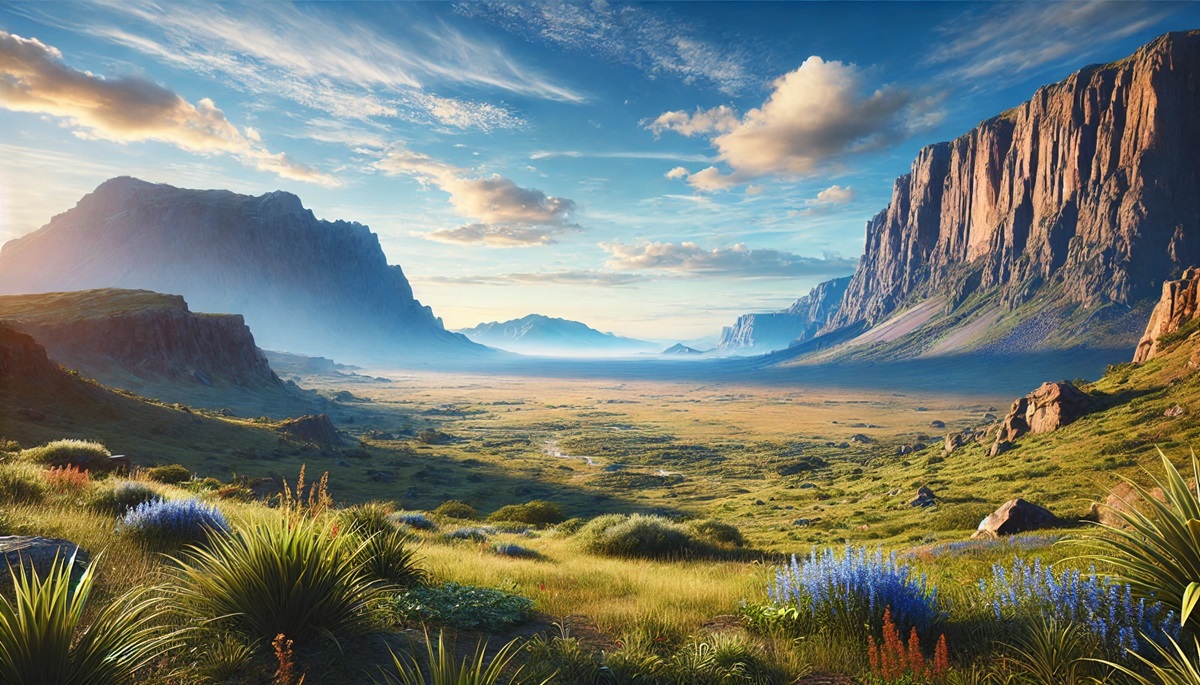
Imagine a vast, elevated landform stretching across the horizon, with flat or gently rolling terrain that stands significantly above the surrounding area. This is a plateau—one of Earth’s most striking geological features. Often referred to as “tablelands” due to their flat appearance, plateaus are fascinating landscapes that come in various shapes, sizes, and altitudes, each telling a story of Earth’s dynamic geological processes.
A plateau is defined as an area of high ground with a flat or nearly flat top, typically rising steeply above the adjacent land. Plateaus can form through a variety of processes, including tectonic activity, volcanic eruptions, and erosion. Found on every continent, plateaus are home to unique ecosystems, vital resources, and human communities. They have played pivotal roles in history, agriculture, and culture, shaping the lives of those who inhabit them.
In this article, we’ll explore the world of plateaus, diving into their types, formation, famous examples, and ecological and cultural significance. Along the way, we’ll uncover intriguing facts and stories that make plateaus some of the most captivating features of our planet.

The Definition and Characteristics of a Plateau
Plateaus are elevated areas of land with relatively flat tops. They are higher than the surrounding terrain and often bordered by steep cliffs or slopes, which make them stand out dramatically in the landscape. Despite their flat appearance, many plateaus have rugged terrain with deep valleys, canyons, and rivers carved by erosion.
Key Features of a Plateau
- Flat or Gently Sloping Top: The defining feature of a plateau is its flat or mildly undulating surface.
- Elevation: Plateaus rise significantly above the surrounding landscape, with steep sides that can range from cliffs to gentle slopes.
- Formation Processes: Plateaus are shaped by various geological processes, including tectonic uplift, volcanic activity, and erosion.
- Varied Ecosystems: Plateaus can support diverse ecosystems, from grasslands to forests, depending on their climate and altitude.
How Are Plateaus Formed?
Plateaus are formed through several geological processes that shape and elevate the Earth’s crust. These processes include tectonic activity, volcanic eruptions, and erosion.
- Tectonic Activity: When tectonic plates collide or move apart, the Earth’s crust can be pushed upward, creating a plateau. This process is responsible for some of the largest plateaus in the world. For example, the Tibetan Plateau, the highest and largest plateau on Earth, was formed when the Indian and Eurasian plates collided.
- Volcanic Activity: Volcanic eruptions can create plateaus by depositing layers of lava over a wide area. Over time, these layers build up to form volcanic plateaus. The Deccan Plateau in India is a prime example of this type of formation.
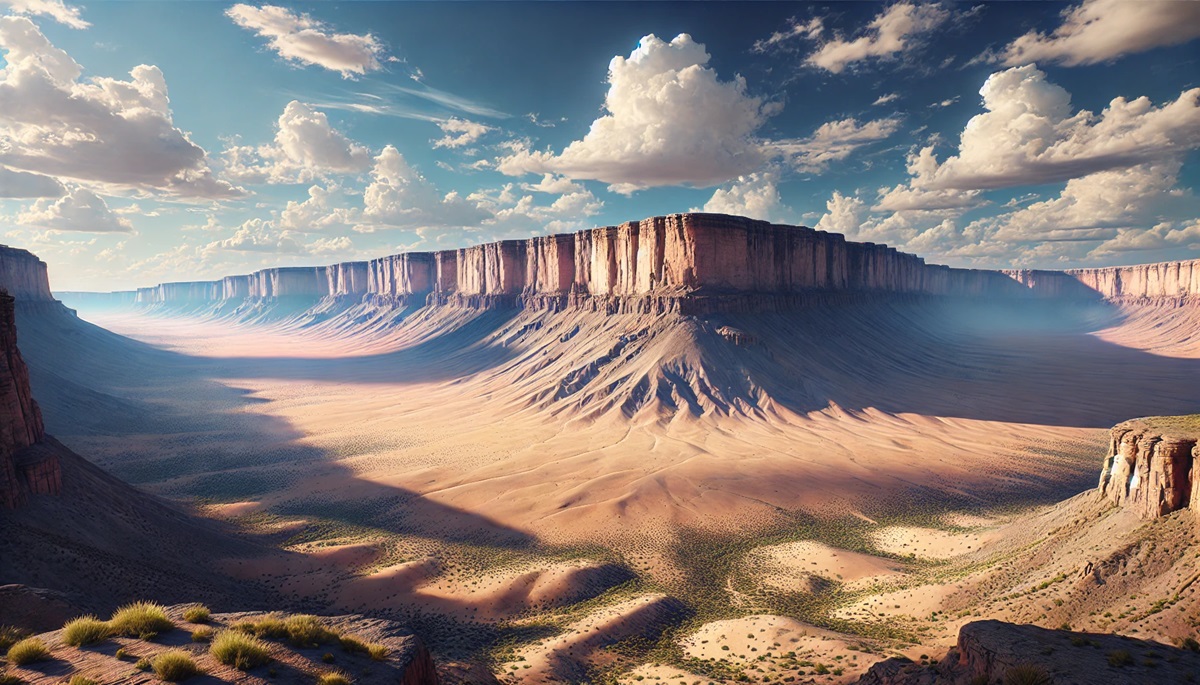
- Erosion: Plateaus can also form through erosion, where softer rock layers are worn away, leaving behind harder, more resistant layers. This process creates dissected plateaus, characterized by rugged terrain and deep valleys. The Colorado Plateau in the United States, home to the Grand Canyon, was shaped by erosion.
- Glacial Activity: In some cases, glacial activity can carve and shape plateaus. As glaciers move and recede, they can leave behind flat-topped landforms surrounded by steep cliffs.
Types of Plateaus
Plateaus can be categorized based on their formation processes and geographical location. Here are the main types:
- Intermontane Plateaus: These plateaus are surrounded by mountains and often lie at very high elevations. The Tibetan Plateau, nestled between the Himalayas and the Kunlun Mountains, is an iconic intermontane plateau.
- Volcanic Plateaus: Formed by successive lava flows, these plateaus are often characterized by volcanic rock and fertile soils. The Columbia Plateau in the United States and the Deccan Plateau in India are examples.
- Dissected Plateaus: These plateaus are heavily eroded, with deep valleys and rugged terrain. The Colorado Plateau, with its stunning canyons and mesas, is a classic dissected plateau.
- Piedmont Plateaus: Located at the base of mountains, piedmont plateaus are formed through uplift and erosion. The Appalachian Plateau in the eastern United States is an example.
Famous Plateaus Around the World
- The Tibetan Plateau: Known as the “Roof of the World,” the Tibetan Plateau is the highest and largest plateau on Earth, covering an area of about 2.5 million square kilometers. It is home to unique ecosystems and cultures, as well as being a critical source of water for Asia’s major rivers.
- The Deccan Plateau: Stretching across southern India, the Deccan Plateau is known for its rich soils, which support agriculture. It is also a region of historical significance, with ancient cities and temples.
- The Colorado Plateau: Located in the southwestern United States, the Colorado Plateau is famous for its dramatic landscapes, including the Grand Canyon, Monument Valley, and Arches National Park.
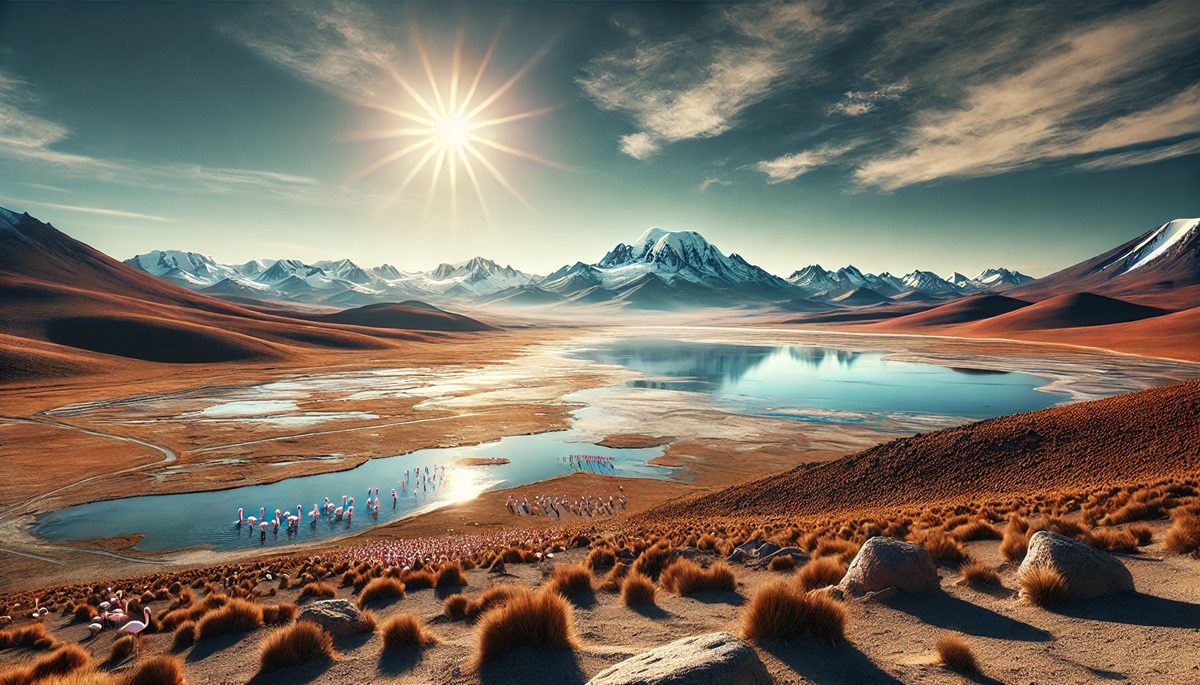
- The Andean Plateaus: The Altiplano in South America is a high plateau nestled between the Andes Mountains. It is known for its breathtaking salt flats, such as Salar de Uyuni, and ancient Incan ruins.
- The Kimberley Plateau: Located in northwestern Australia, the Kimberley Plateau is a remote and rugged region known for its unique wildlife, gorges, and Aboriginal rock art.
Plateaus in History and Culture
Plateaus have played significant roles in human history and culture, serving as centers of civilization, agriculture, and trade. Their elevated terrain often provided natural defense against invaders, while their fertile soils supported agriculture.
- Cradles of Civilization: Plateaus like the Deccan Plateau in India and the Ethiopian Highlands in Africa have been home to ancient civilizations. These regions benefited from their fertile soils and strategic locations.
- Sacred Landscapes: Many cultures have viewed plateaus as sacred spaces. The Tibetan Plateau, for example, is central to Tibetan Buddhism, with its monasteries and spiritual significance.
- Trade and Commerce: Plateaus have historically served as hubs for trade due to their strategic locations. The Andean Plateaus, for instance, were vital to the Incan Empire’s trade network.
Fun Facts About Plateaus
The Largest Plateau: The Tibetan Plateau is not only the largest but also the highest plateau in the world, with an average elevation of 4,500 meters (14,800 feet).
Plateaus on Other Planets: Mars has plateaus too! The Tharsis Plateau is home to the largest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons.
Volcanic Riches: Volcanic plateaus, like the Deccan Plateau, are often rich in minerals and fertile soils, making them agricultural hotspots.
Climate Diversity: Plateaus can experience a wide range of climates, from arid conditions in the Altiplano to cold, snowy winters on the Tibetan Plateau.
The Role of Plateaus in Ecosystems
Plateaus support diverse ecosystems, from grasslands to forests, depending on their altitude, climate, and location. These ecosystems are home to unique species adapted to the specific conditions of plateaus.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Plateaus like the Ethiopian Highlands are biodiversity hotspots, home to rare species such as the Ethiopian wolf and gelada baboon.
- Water Sources: Many plateaus are critical sources of water for rivers and lakes. The Tibetan Plateau, often called the “Third Pole,” feeds major Asian rivers like the Yangtze, Ganges, and Mekong.
- Agricultural Importance: Fertile soils on volcanic plateaus make them ideal for farming. The Deccan Plateau, for instance, is a major agricultural region in India.
Environmental Challenges Facing Plateaus
Despite their resilience, plateaus face numerous environmental challenges:
- Deforestation: Logging and agriculture threaten plateau ecosystems, leading to soil erosion and habitat loss.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures are impacting plateau ecosystems, particularly in high-altitude regions like the Tibetan Plateau.
- Mining: Many plateaus are rich in minerals, but mining can lead to environmental degradation and loss of biodiversity.
- Urbanization: Human settlement and infrastructure development on plateaus can disrupt natural ecosystems.
Conclusion: Guardians of Earth’s Natural Heritage
Plateaus are much more than elevated landforms—they are vital components of Earth’s geography, supporting ecosystems, cultures, and economies. From the breathtaking vistas of the Colorado Plateau to the spiritual significance of the Tibetan Plateau, these tablelands inspire awe and serve as reminders of the Earth’s dynamic processes.
As we explore and utilize plateaus, it is crucial to protect their unique ecosystems and cultural heritage. By understanding and appreciating plateaus, we ensure that their beauty and importance endure for generations to come. Whether gazing at the Grand Canyon or traversing the Andean Highlands, plateaus remind us of the power and splendor of nature.














